Serial To Parallel Shift Register
- Serial To Parallel Converter Circuit
- 16 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register
- Parallel In Serial Out Register
- 8 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register
- 32 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register
The 74LV165A is an 8-bit parallel-load or serial-in shift register with complementary serial outputs (Q7 and Q7) available from the last stage. When the parallel-load input (PL) is LOW, parallel data from the inputs D0 to D7 are loaded into the register asynchronously. When input PL is HIGH, data enters the register seria lly at the input DS. Generally, shift registers operate in one of four different modes with the basic movement of data through a shift register being: Serial-in to Parallel-out (SIPO) - the register is loaded with serial data, one bit at a time. Serial-in to Serial-out (SISO) - the data is shifted serially 'IN'. VHDL nbit - 8 bit serial to parallel shift register code test in circuit and test bench ISE Xilinx This video is part of a series which final design is a Controlled Datapath using a structural approach. Generally, shift registers operate in one of four different modes with the basic movement of data through a shift register being: Serial-in to Parallel-out (SIPO) - the register is loaded with serial data, one bit at a time. Serial-in to Serial-out (SISO) - the data is shifted serially 'IN'.
- Serial In Serial Out shift register; Serial In Parallel Out shift register; Parallel In Parallel Out shift register; Parallel In Serial Out shift register; So to quickly summarize a few things. Shift registers are a series of flip-flops connected together through which data shifts. They have four main types.
- 16 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register DOWNLOAD (Mirror #1) 500 Terry Francois Street, San Francisco, CA 94158 1-800-000-0000.
Library
When a high level is applied to this pin, the shift register is allowed to serially shift data. When a low level is applied to this pin, the shift register accepts parallel data from the data latch. Shift Clock (Pin 11) Serial shift clock.
Simscape / Electrical / Specialized Power Systems / Control & Measurements / Additional Components
Description
The Discrete Shift Register block outputs a vector containingthe last N samples of the input signal. When the input contains morethan one signal, the block outputs the last N samples of each signalin the following order:
Out = [u1(k), u1(k−1), u1(k−2), u1(k−3),u2(k), u2(k−1), u2(k−2), u2(k−3)]
This example shows the block output for an input containingtwo signals, represented by u1 and u2, and a number of samples N =4, represented by the k to k−3 indices. The dimension of theoutput vector is 4 × 2 = 8.
Parameters
Specify the number of samples, or stages, of the register. Theminimum value is 1. Default is 32.
Specify the initial value of the N-1 samples preceding time 0.Enter a scalar value or a vector of the same size as the input signal.Default is 0.
Specify the time interval between the samples. Default is 50e-6.
Serial To Parallel Converter Circuit
Characteristics
| Direct Feedthrough | Yes |
| Sample Time | Discrete |
| Dimensionalized | Yes |
| Scalar Expansion | Yes, of the parameter Initial inputs |
| Zero-Crossing Detection | No |
Examples
The power_DiscreteShiftRegister exampleshows various uses of the Discrete Shift Register block.
- Digital Circuits Tutorial
- Digital Circuits Resources
- Selected Reading
We know that one flip-flop can store one-bit of information. In order to store multiple bits of information, we require multiple flip-flops. The group of flip-flops, which are used to hold (store) the binary data is known as register.
Now look, if you’ve managed to get Cydia installer iOS 12.1.1, you should head to the installer app and download jailbreak apps that I’ve listed above in the first half, but the real thing is if you haven’t jailbroken your iPhone X till now and wanna know how to get free jailbreak apps or paid apps from App Store for free on iPhone X. To get free in-app purchase just tap on whatever you want, like the coin, gem for games and free services for applications. Just tap on it and it will ask you to enter your Apple ID and on that point just hit cancel and then you will have your purchase without losing money. Appandora App Library is a free but powerful iOS App Manager, which enables users to download and install jailbreak and free apps directly to your iPad/iPhone/iPod instead of using App store. The tutorial will guide you how to get jailbreak apps for free on your iOS devices with Appandora App Library. Jul 12, 2018 HOW TO GET PAID APPS FREE FROM THE APPSTORE JAILBREAK NEEDED ON iOS 8/9/10/11/11.4 Beta's Link - Not showing up? Use this link to. Download & install best free apps for ios from the App Store iPhone, iPod Touch, or iPad No Jailbreak / PC iOS 12 - 12.4 & 12.2 / 11 / 10 / 9 free! Get free apps jailbreak.
If the register is capable of shifting bits either towards right hand side or towards left hand side is known as shift register. An ‘N’ bit shift register contains ‘N’ flip-flops. Following are the four types of shift registers based on applying inputs and accessing of outputs.
- Serial In − Serial Out shift register
- Serial In − Parallel Out shift register
- Parallel In − Serial Out shift register
- Parallel In − Parallel Out shift register
Serial In − Serial Out (SISO) Shift Register
The shift register, which allows serial input and produces serial output is known as Serial In – Serial Out (SISO) shift register. The block diagram of 3-bit SISO shift register is shown in the following figure.
This block diagram consists of three D flip-flops, which are cascaded. That means, output of one D flip-flop is connected as the input of next D flip-flop. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since, the same clock signal is applied to each one.
In this shift register, we can send the bits serially from the input of left most D flip-flop. Hence, this input is also called as serial input. For every positive edge triggering of clock signal, the data shifts from one stage to the next. So, we can receive the bits serially from the output of right most D flip-flop. Hence, this output is also called as serial output.
Example
16 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register
Let us see the working of 3-bit SISO shift register by sending the binary information “011” from LSB to MSB serially at the input.
Assume, initial status of the D flip-flops from leftmost to rightmost is $Q_{2}Q_{1}Q_{0}=000$. We can understand the working of 3-bit SISO shift register from the following table.
| No of positive edge of Clock | Serial Input | Q2 | Q1 | Q0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1(LSB) | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0(MSB) | 0 | 1 | 1(LSB) |
| 4 | - | - | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | - | - | - | 0(MSB) |
The initial status of the D flip-flops in the absence of clock signal is $Q_{2}Q_{1}Q_{0}=000$. Here, the serial output is coming from $Q_{0}$. So, the LSB (1) is received at 3rd positive edge of clock and the MSB (0) is received at 5th positive edge of clock.
Therefore, the 3-bit SISO shift register requires five clock pulses in order to produce the valid output. Similarly, the N-bit SISO shift register requires 2N-1 clock pulses in order to shift ‘N’ bit information.
Serial In - Parallel Out (SIPO) Shift Register
The shift register, which allows serial input and produces parallel output is known as Serial In – Parallel Out (SIPO) shift register. The block diagram of 3-bit SIPO shift register is shown in the following figure.
This circuit consists of three D flip-flops, which are cascaded. That means, output of one D flip-flop is connected as the input of next D flip-flop. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since, the same clock signal is applied to each one.
In this shift register, we can send the bits serially from the input of left most D flip-flop. Hence, this input is also called as serial input. For every positive edge triggering of clock signal, the data shifts from one stage to the next. In this case, we can access the outputs of each D flip-flop in parallel. So, we will get parallel outputs from this shift register.
Example
Let us see the working of 3-bit SIPO shift register by sending the binary information “011” from LSB to MSB serially at the input.
Assume, initial status of the D flip-flops from leftmost to rightmost is $Q_{2}Q_{1}Q_{0}=000$. Here, $Q_{2}$ & $Q_{0}$ are MSB & LSB respectively. We can understand the working of 3-bit SIPO shift register from the following table.
| No of positive edge of Clock | Serial Input | Q2(MSB) | Q1 | Q0(LSB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1(LSB) | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 0(MSB) | 0 | 1 | 1 |
The initial status of the D flip-flops in the absence of clock signal is $Q_{2}Q_{1}Q_{0}=000$. The binary information “011”Activinspire free download for teachers. is obtained in parallel at the outputs of D flip-flops for third positive edge of clock.
So, the 3-bit SIPO shift register requires three clock pulses in order to produce the valid output. Similarly, the N-bit SIPO shift register requires N clock pulses in order to shift ‘N’ bit information.
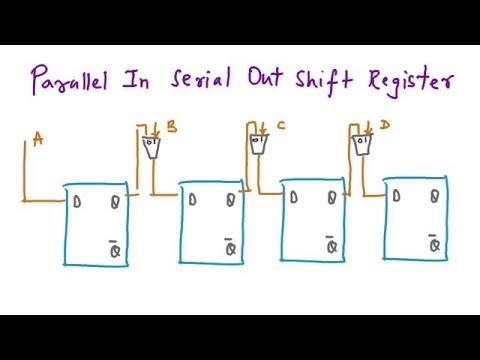
Parallel In − Serial Out (PISO) Shift Register
The shift register, which allows parallel input and produces serial output is known as Parallel In − Serial Out (PISO) shift register. The block diagram of 3-bit PISO shift register is shown in the following figure.
This circuit consists of three D flip-flops, which are cascaded. That means, output of one D flip-flop is connected as the input of next D flip-flop. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since, the same clock signal is applied to each one.
In this shift register, we can apply the parallel inputs to each D flip-flop by making Preset Enable to 1. For every positive edge triggering of clock signal, the data shifts from one stage to the next. So, we will get the serial output from the right most D flip-flop.
Example
Let us see the working of 3-bit PISO shift register by applying the binary information “011” in parallel through preset inputs.
Since the preset inputs are applied before positive edge of Clock, the initial status of the D flip-flops from leftmost to rightmost will be $Q_{2}Q_{1}Q_{0}=011$. We can understand the working of 3-bit PISO shift register from the following table.
| No of positive edge of Clock | Q2 | Q1 | Q0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1(LSB) |
| 1 | - | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | - | - | 0(LSB) |
Here, the serial output is coming from $Q_{0}$. So, the LSB (1) is received before applying positive edge of clock and the MSB (0) is received at 2nd positive edge of clock.
Parallel In Serial Out Register
Therefore, the 3-bit PISO shift register requires two clock pulses in order to produce the valid output. Similarly, the N-bit PISO shift register requires N-1 clock pulses in order to shift ‘N’ bit information.
Parallel In - Parallel Out (PIPO) Shift Register
The shift register, which allows parallel input and produces parallel output is known as Parallel In − Parallel Out (PIPO) shift register. The block diagram of 3-bit PIPO shift register is shown in the following figure.
This circuit consists of three D flip-flops, which are cascaded. That means, output of one D flip-flop is connected as the input of next D flip-flop. All these flip-flops are synchronous with each other since, the same clock signal is applied to each one.
8 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register
In this shift register, we can apply the parallel inputs to each D flip-flop by making Preset Enable to 1. We can apply the parallel inputs through preset or clear. These two are asynchronous inputs. That means, the flip-flops produce the corresponding outputs, based on the values of asynchronous inputs. In this case, the effect of outputs is independent of clock transition. So, we will get the parallel outputs from each D flip-flop.
32 Bit Serial To Parallel Shift Register
Example
Let us see the working of 3-bit PIPO shift register by applying the binary information “011” in parallel through preset inputs.
Since the preset inputs are applied before positive edge of Clock, the initial status of the D flip-flops from leftmost to rightmost will be $Q_{2}Q_{1}Q_{0}=011$. So, the binary information “011” is obtained in parallel at the outputs of D flip-flops before applying positive edge of clock.
Therefore, the 3-bit PIPO shift register requires zero clock pulses in order to produce the valid output. Similarly, the N-bit PIPO shift register doesn’t require any clock pulse in order to shift ‘N’ bit information.